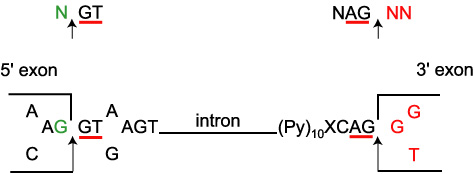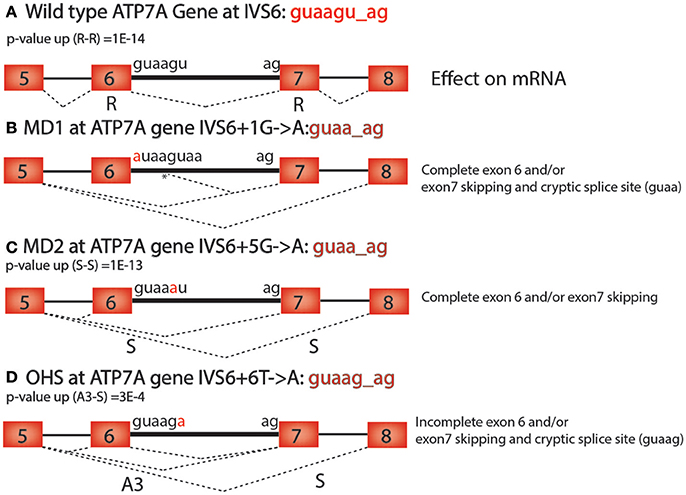
Frontiers | A Bioinformatics-Based Alternative mRNA Splicing Code that May Explain Some Disease Mutations Is Conserved in Animals
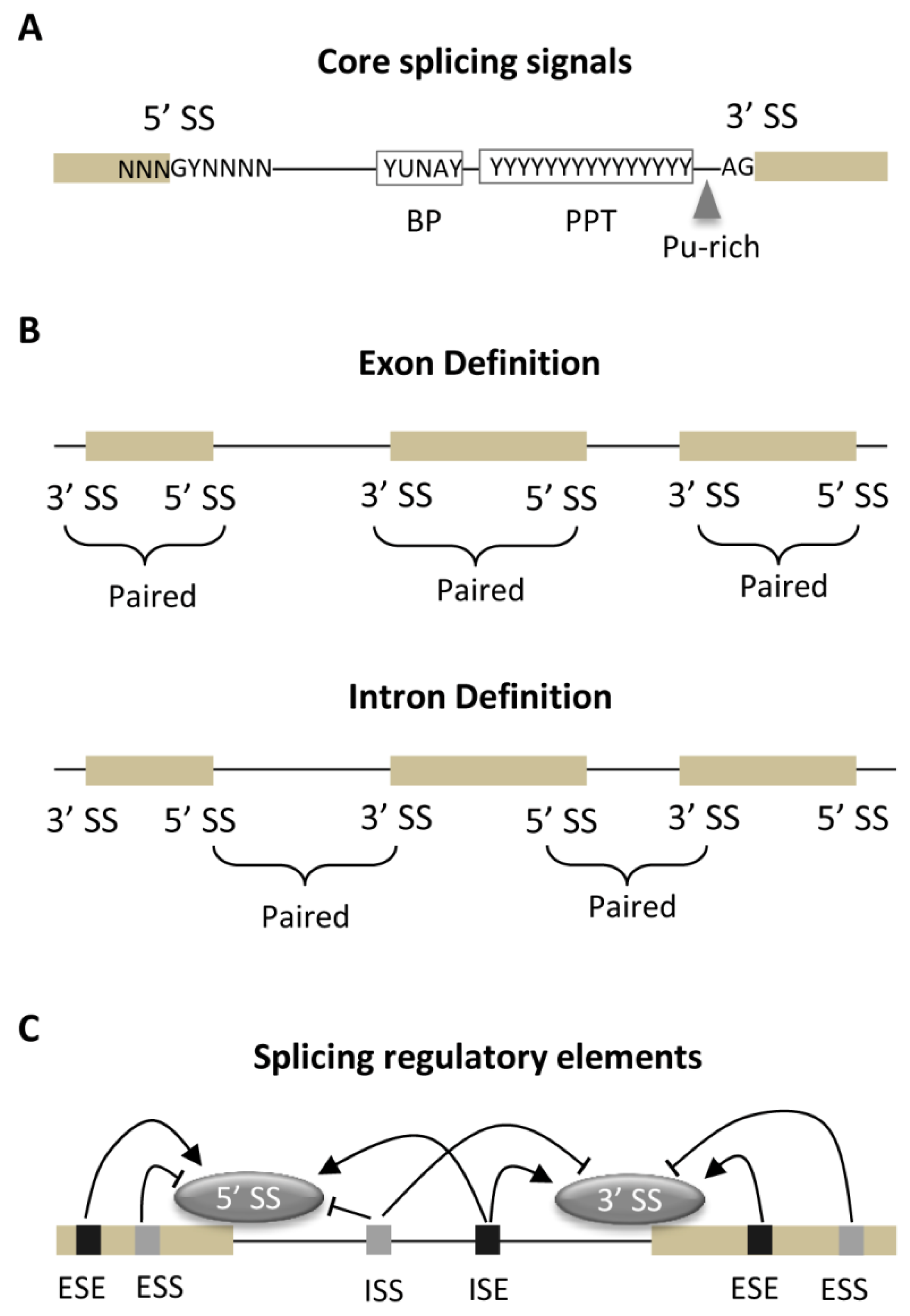
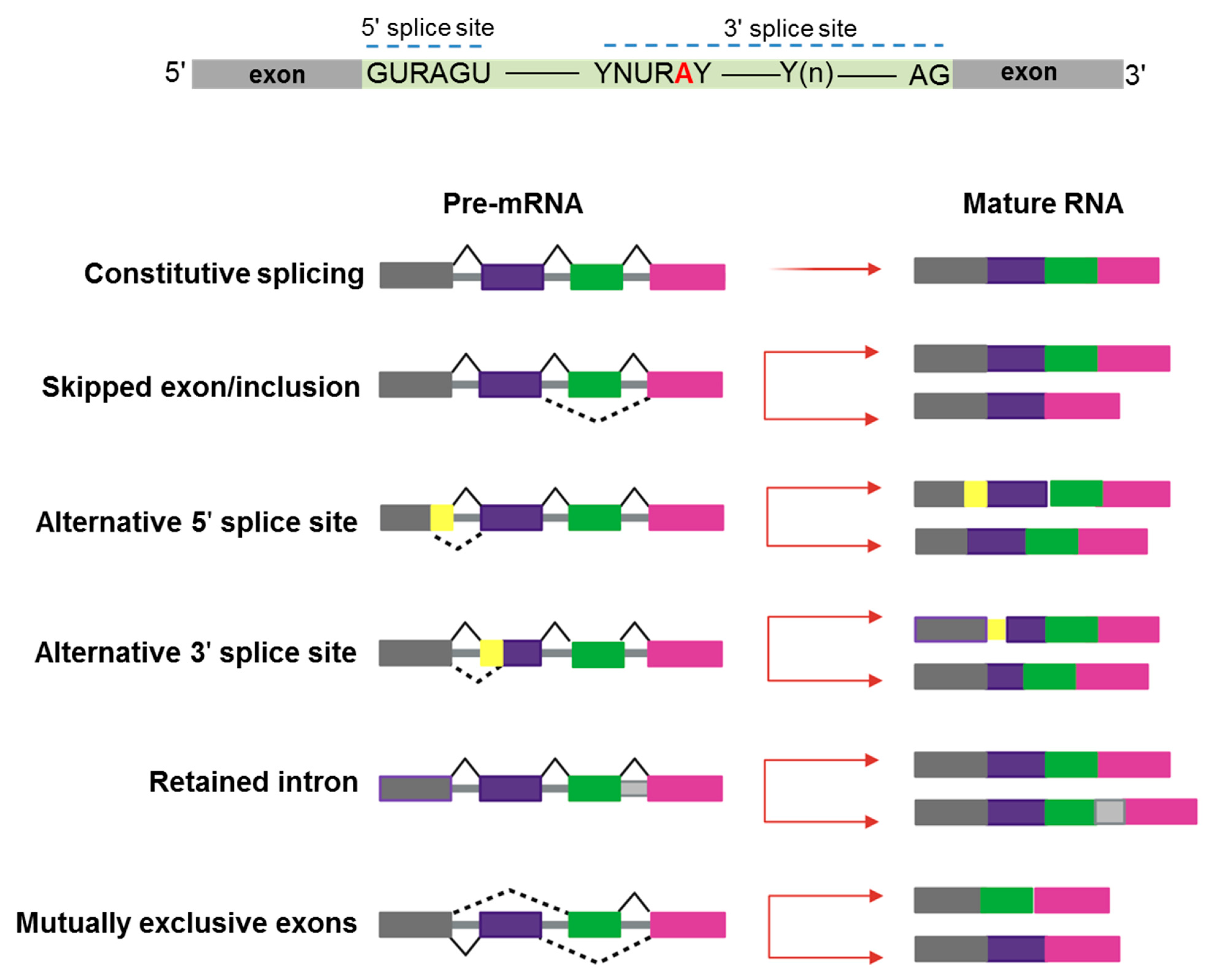
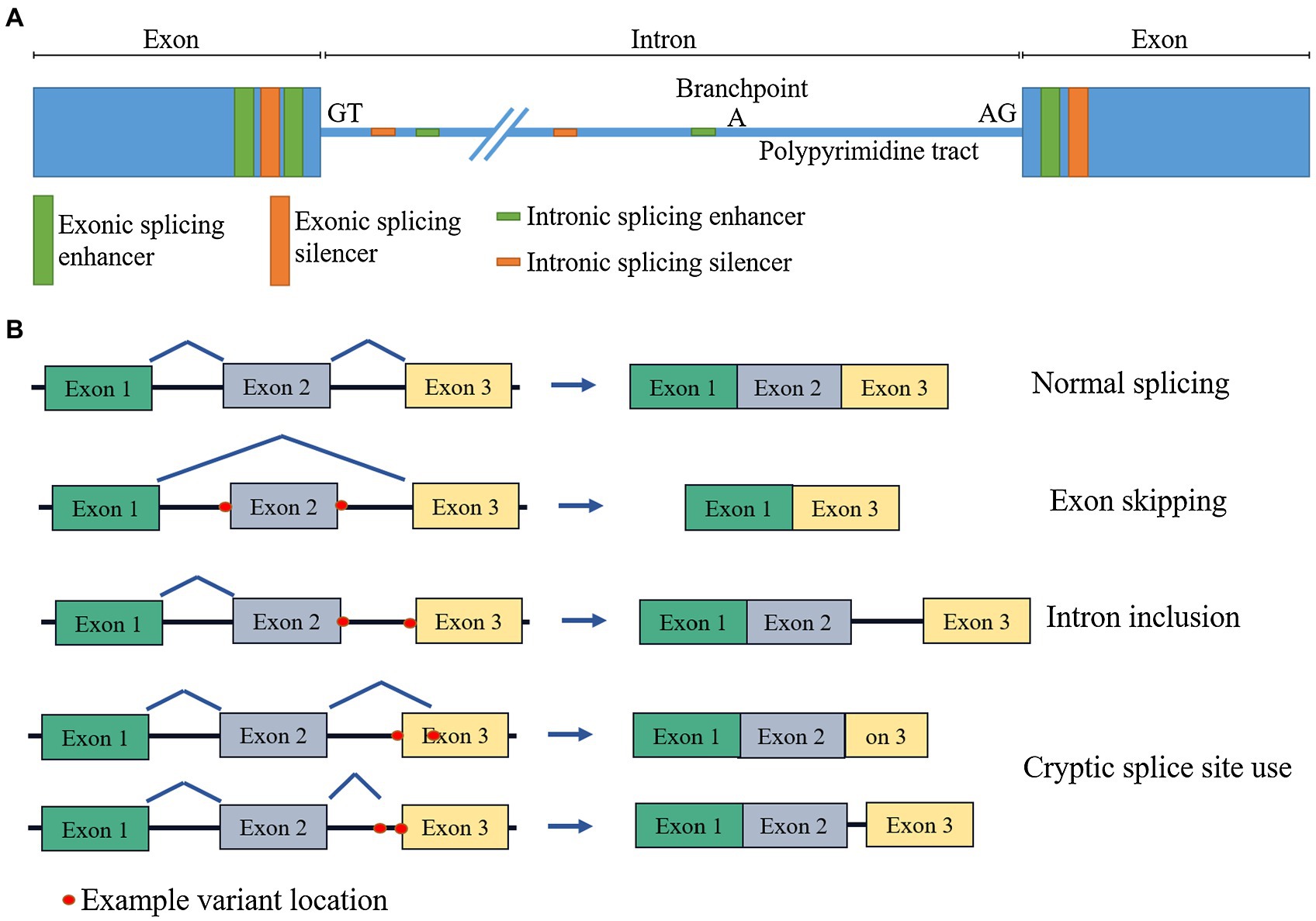
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Sequence and Evolutionary Features for the Alternatively Spliced Exons of Eukaryotic Genes

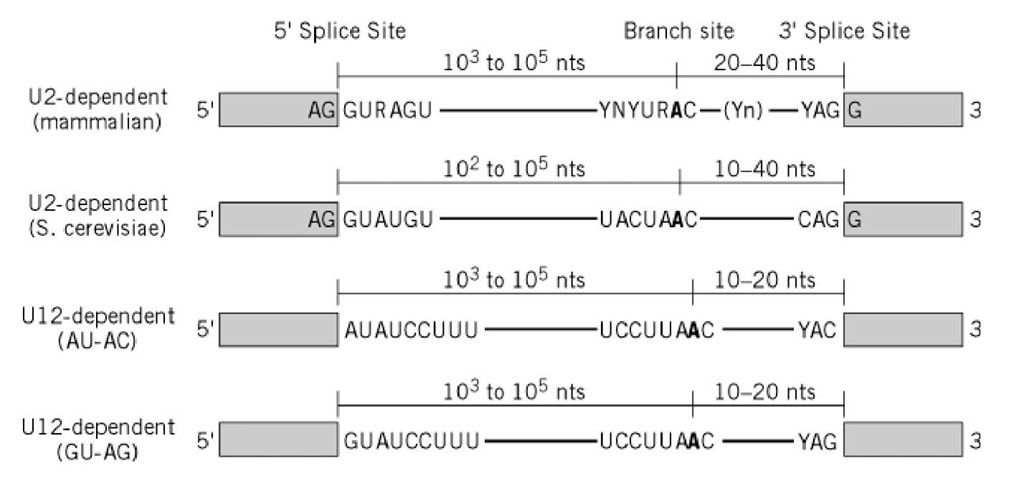
Splice site consensus sequences for U2-dependent (a) and U12-dependent... | Download Scientific Diagram
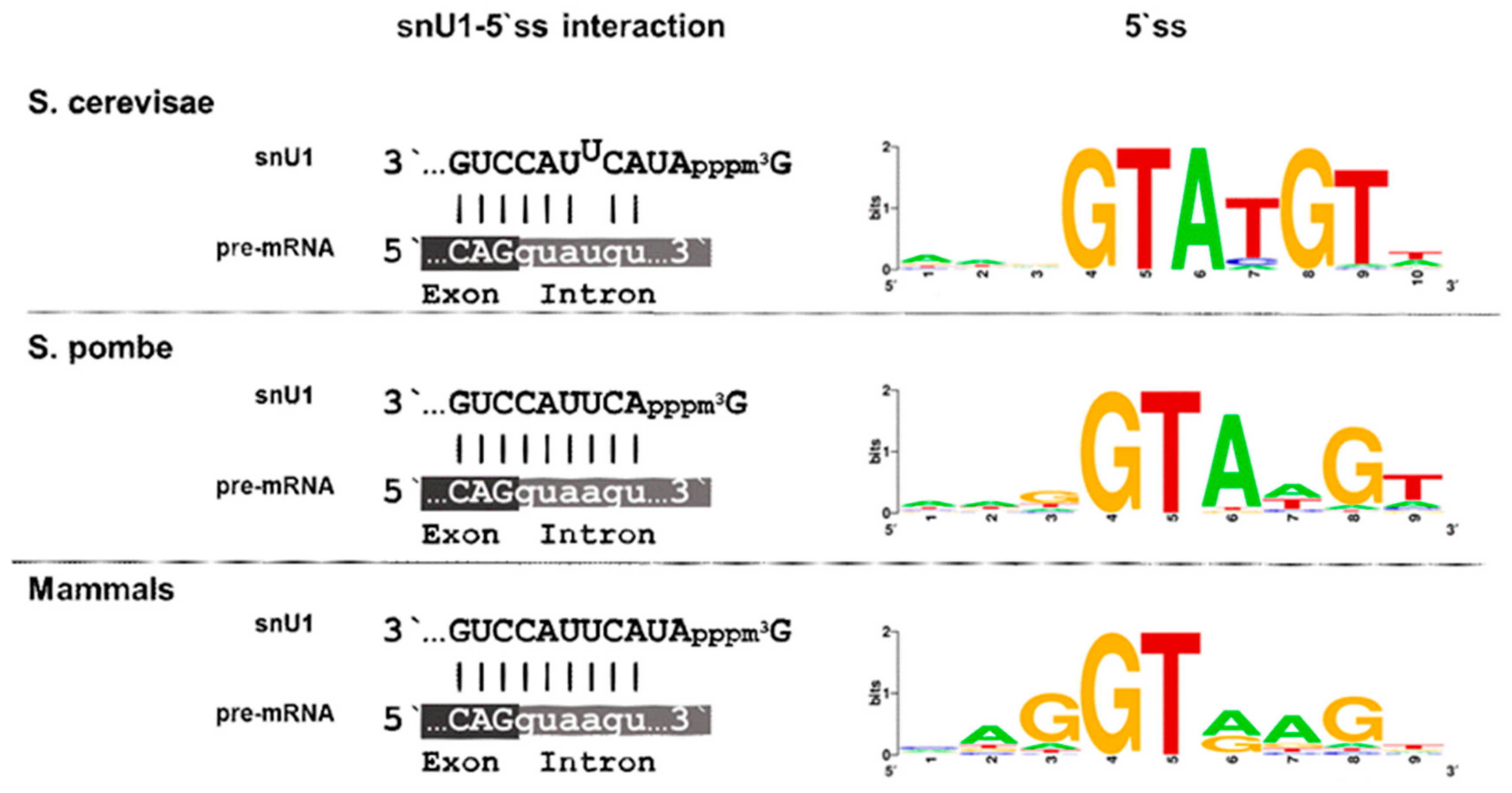
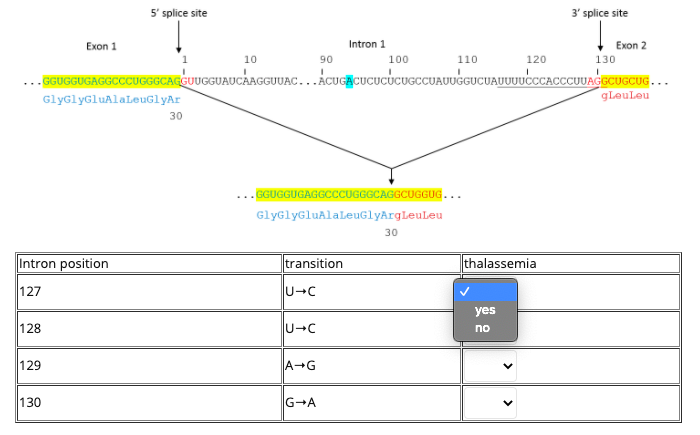
A genetic screen in C. elegans reveals roles for KIN17 and PRCC in maintaining 5' splice site identity | PLOS Genetics
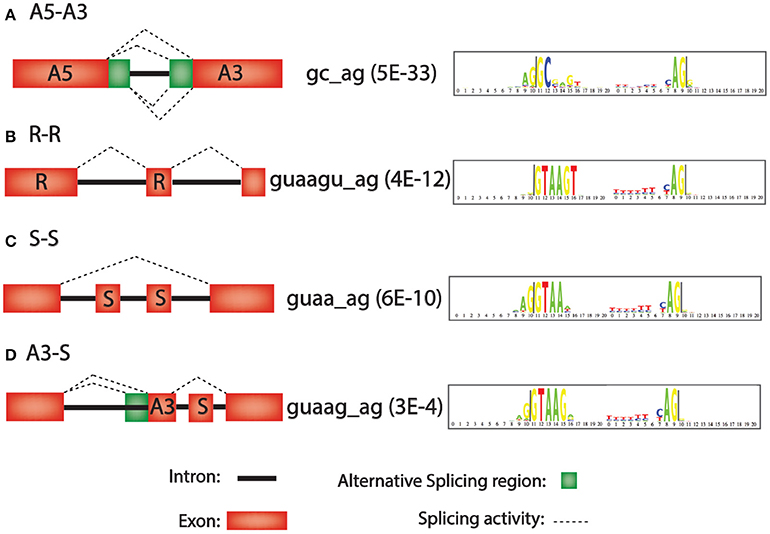
Frontiers | A Bioinformatics-Based Alternative mRNA Splicing Code that May Explain Some Disease Mutations Is Conserved in Animals
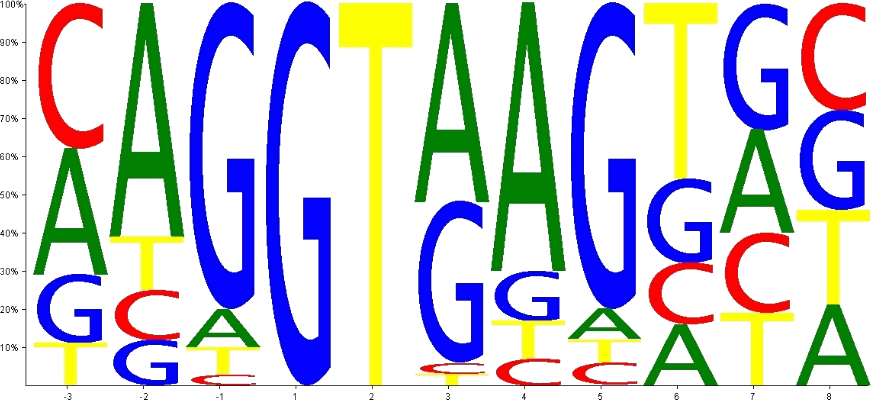
Oriented Scanning Is the Leading Mechanism Underlying 5′ Splice Site Selection in Mammals | PLOS Genetics

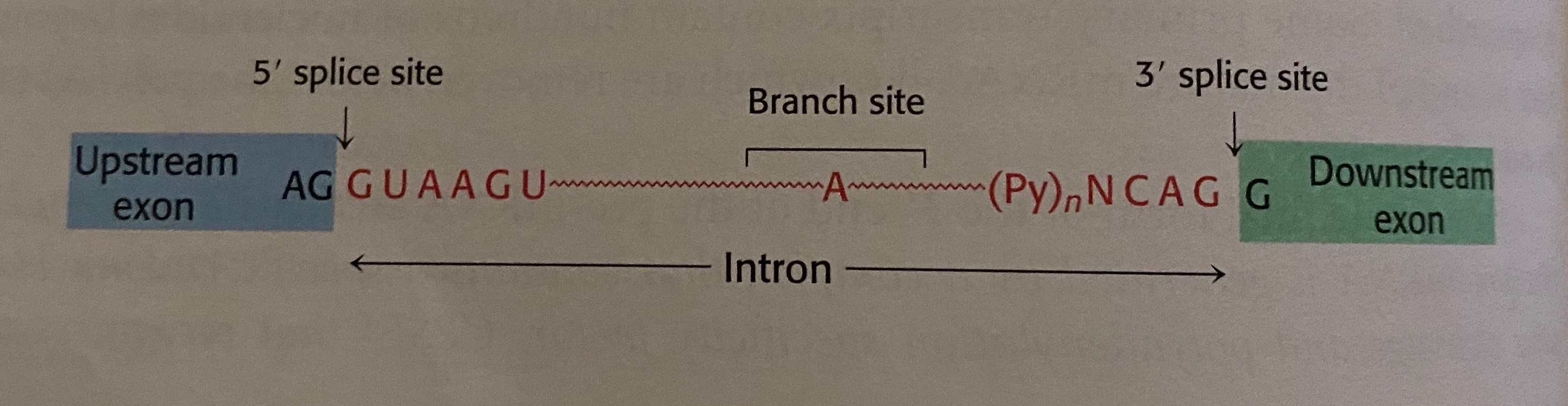
Branch Point Identification and Sequence Requirements for Intron Splicing in Plasmodium falciparum | Eukaryotic Cell

Consensus sequence analysis of (back-)splice sites and prediction of... | Download Scientific Diagram

Consensus sequences of human U12- and U2-type introns. The height of... | Download Scientific Diagram

A) Consensus splice site sequences of minor and major introns. Minor... | Download Scientific Diagram